[ad_1]

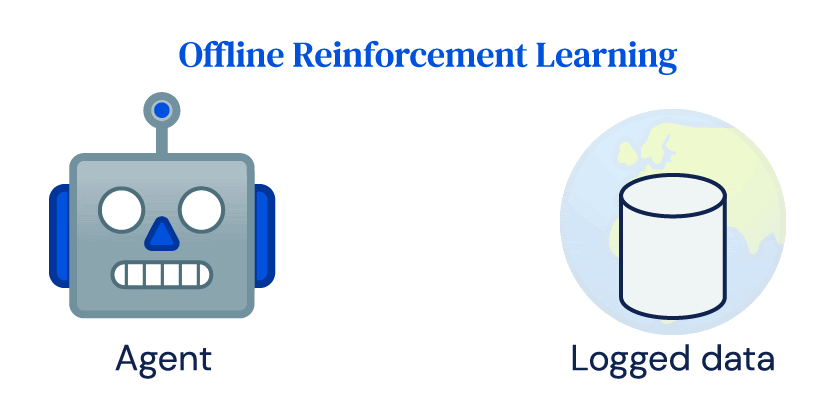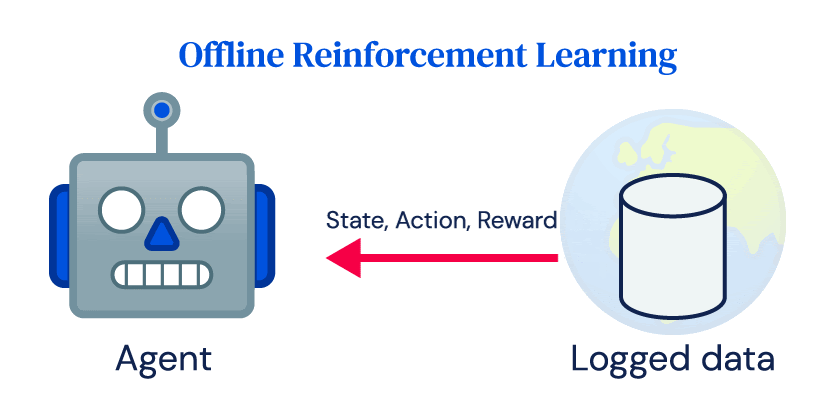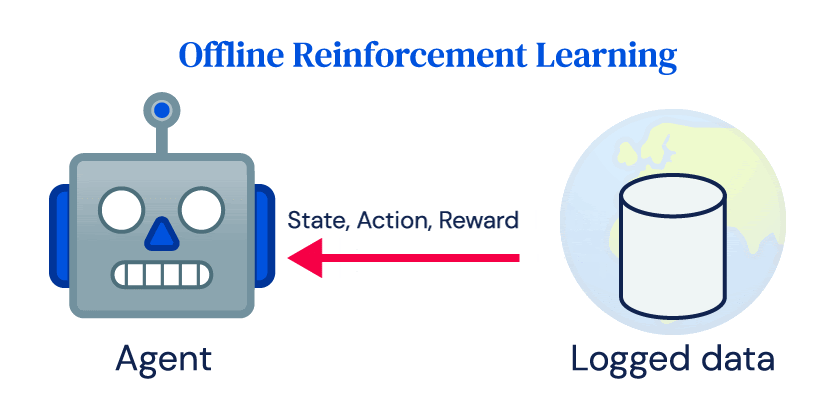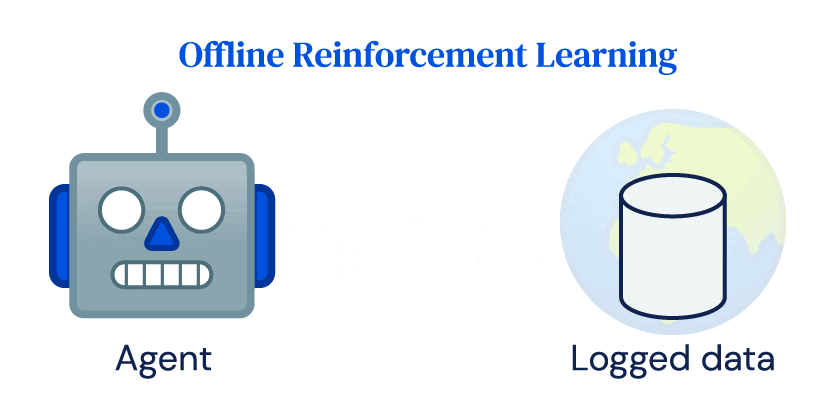
Many of the successes of RL rely heavily on repeated online interactions of an agent with an environment, which we call online RL. Despite its success in simulation, the uptake of RL for real-world applications has been limited. Power plants, robots, healthcare systems, or self-driving cars are expensive to run and inappropriate controls can have dangerous consequences. They are not easily compatible with the crucial idea of exploration in RL and the data requirements of online RL algorithms. Nevertheless, most real-world systems produce large amounts of data as part of their normal operation, and the goal of offline RL to learn a policy directly from that logged data without interacting with the environment.
Offline RL methods (e.g Agarwal et al., 2020; Fujimoto et al., 2018) have shown promising results on well-known benchmark domains. However, non-standardised evaluation protocols, differing datasets, and ack of baselines make algorithmic comparisons difficult. Nevertheless, some important properties of potential real-world application domains such as partial observability, high-dimensional sensory streams (i.e., images), diverse action spaces, exploration problems, non-stationarity, and stochasticity, are underrepresented in the current offline RL literature.
[INSERT GIF + CAPTION]
We introduce a novel collection of task domains and associated datasets together with a clear evaluation protocol. We include widely-used domains such as the DM Control Suite (Tassa et al., 2018) and Atari 2600 games (Bellemare et al., 2013), but also domains that are still challenging for strong online RL algorithms such as real-world RL (RWRL) suite tasks (Dulac-Arnold et al., 2020) and DM Locomotion tasks (Heess et al., 2017; Merel et al., 2019a,b, 2020). By standardizing the environments, datasets, and evaluation protocols, we hope to make research in offline RL more reproducible and accessible. We call our suite of benchmarks “RL Unplugged”, because offline RL methods can use it without any actors interacting with the environment. Our paper offers four main contributions: (i) a unified API for datasets (ii) a varied set of environments (iii) clear evaluation protocols for offline RL research, and (iv) reference performance baselines.
RL Unplugged: Benchmarks for Offline Reinforcement Learning
[ad_2]
Source link